What Are the Types of Casting?
Casting is a fabrication method where molten metal is poured into predesigned molds with the desired shape and left to solidify to create a component. The finished part is referred to as a casting. This part is achieved by destroying or breaking the mold after solidification.
In most cases, casting materials are usually metals or metal alloys with the ability to cure when mixed with two or more elements. Casting is mainly used to produce parts with complex designs and shapes, which cannot be achieved through other methods.
Contents
Examples of casting processes
Casting remains one of the age-old metal fabrication techniques. However, the method has undergone evolutions over the years due to technological advancements. Nowadays, there are many types of casting used in different industries. All casting processes come with advantages and disadvantages that make them suitable for particular applications. Below are the most popular types of casting processes.
1. Investment casting
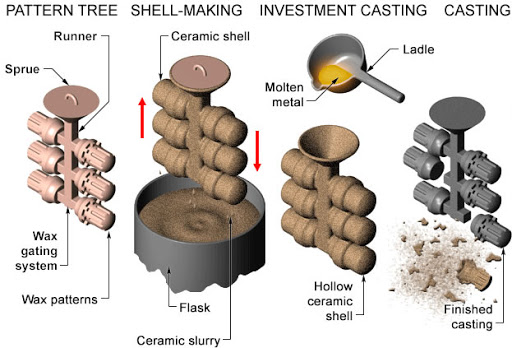
Investment casting is also called lost wax casting, precision casting, or lost form casting. The investment casting process involves injecting wax in predesigned molds and then coating it with a refractory material, mainly a ceramic slurry. The wax is removed by heating it to melt out. Next, the refractory shell is broken to get the finished piece.
Investment casting applications include manufacturing metal components with complex shapes and designs in the defense, medical, food, automotive, and aerospace industries. Accordingly, the advantages of precision casting are:
- Excellent surface finish
- A high degree of precision
- Can produce parts with complex dimensions
- It can be used with both ferrous and non-ferrous metals
Despite these advantages, precision casting can be relatively costly than other casting methods. However, the overall production cost is reduced since the technique does not require post-processes.
2. Die casting
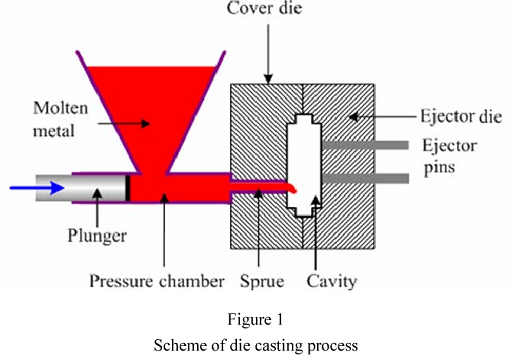
Die casting is a metal fabrication technique that requires high pressure. Accordingly, the process is mainly used with non-ferrous metals.
The mold used in die casting is usually coated with a lubricant to control the temperatures around the die. Molten metal is then poured using high pressure. The process continues as solidification takes place. After solidification, the part is removed from the die.
The advantages of die casting include:
- High dimensional consistency and uniformity in design
- It does not necessarily require post-processes
- Excellent shape and size tolerances
Die casting also has its drawbacks. This includes high tooling costs. Additionally, it is challenging to ensure structural and mechanical properties are achieved. Lastly, die casting can only be used for products that do not require the mold destroyed during the removal stage.
3. Sand Casting
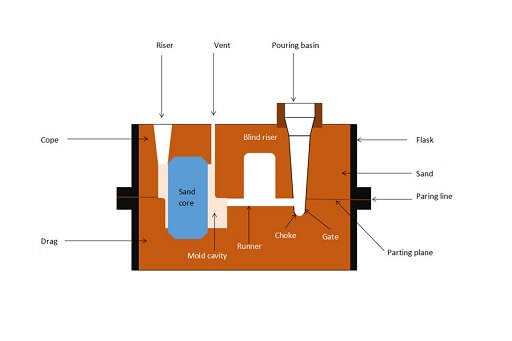
Sand casting is a casting technique that relies on silica-based material or bonded sand. When sand is used to make molds, it has to be finely ground and impacted with clay or any other binding material.
Sand casting is generally meant to minimize tearing and cracking in the finished part. This also ensures the product has a degree of shrinkage and flexibility.
Sand casting is used to manufacture products, such as engine blocks.
The steps involved in the sand casting process are usually the same as other casting processes. The only difference is found in the mold-making stage.
The advantages of sand casting include:
- Relatively affordable when manufacturing low volumes.
- It can be used to produce larger components.
- It can be used with many metals and alloys.
Despite the benefits of sand casting, the process also has disadvantages. For instance, the weaknesses of sand casting include low precision. Additionally, the process is not suitable for components with complex shapes, sizes, and designs.
4. Plaster casting
Plaster casting comes closer to sand casting in various aspects. For instance, the method relies on a mold strengthened with a binding material and gypsum. The plaster cannot stick on the mold because it is coated with an anti-sticking compound.
The advantages of plaster casting include:
- Smooth surface finish
- Can produce materials with intricate shapes and thin walls
- Relatively less costly when producing larger parts
- High dimensional precision
The plaster casting can be expensive since the plaster must be replaced after every session. This is because it forms defects once used. Additionally, plaster casting applications are limited to parts made of aluminum and copper alloys.
5. Centrifugal casting
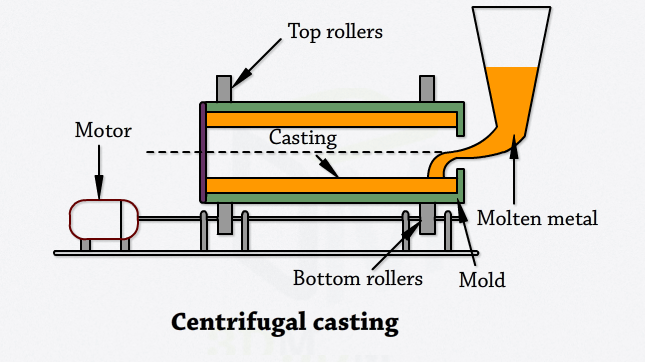
Centrifugal casting is one of the unique casting methods of metal fabrication. The process is most suitable for manufacturing long, cylindrical components with consistent diameters and thin walls.
The centrifugal casting process involves pouring molten metal into rotating molds. The rotation helps the molten metal stick to the mold’s walls, allowing for the manufacture of thin-walled parts. Accordingly, the mold may be designed using sand or metal, depending on the part being produced and the material used to produce it.
Accordingly, there are two main types of centrifugal casting. These are vertical centrifugal casting and horizontal centrifugal casting. When the mold used rotates on a vertical axis, the process is vertical centrifugal casting. On the other hand, when the mold rotates on a horizontal axis, horizontal centrifugal casting occurs.
Centrifugal casting applications depend on what is produced and the material used. Generally, the process is used in many industries, such as the agricultural, aerospace, and automotive sectors.
6. Permanent mold casting

Permanent mold casting takes almost the same shape as die casting and centrifugal casting. This is because the process uses molds that are not destroyed during the casting process. The permanent casting process can fabricate components using different materials, such as aluminum, steel, and zinc alloys.
Generally, the permanent casting process is a low-pressure technique where molten metal is poured manually on a turntable. The molds are coated, filled, and emptied as they rotate through different phases.
Final Thoughts
It is essential to consult with a casting manufacturer to determine the type of casting suitable for your projects. However, you should keep in mind that if your application requires a ferrous metal, the most suitable casting process has to be one that uses expandable molds.
Accordingly, you should visit the casting foundry to have firsthand experience with the casting company and its processes. This will help you choose the best manufacturer with excellent processes. Knowing what you want in terms of size, shape complexity, surface finish, and design integrity will also help you determine the best casting type.
