Contents
Types of Casting Defects and How to Prevent Them
Cast metal parts can leave the factory with defects that lead to a slew of customer complaints. Casting defects are common. But, how can you prevent these casting defects?
Metal casting is a complex process. Every level manufacturing stage has its complexities and technicalities. Accordingly, the finished product quality also depends on the operators’ skill levels, the management, and the quality of the equipment used.
What Is a Casting Defect?
Casting defects are unwanted irregularities that appear on the finished part during the casting process. Many things can lead to casting defects. Accordingly, this article discusses different types of casting defects and how to prevent them.
Types of Casting Defects
Here are the different types of casting defects and their remedies:
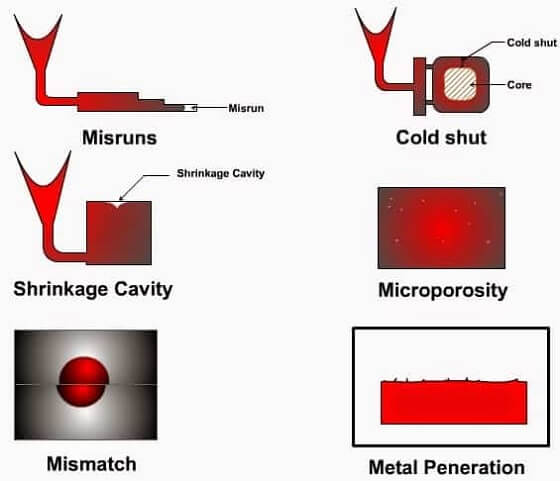
1. Defects in Casting Shrinkage

Metal alloys often shrink during the cooling process that leads to solidification. There are three types of casting shrinkage defects:
- Open Shrinkage Defects: Open shrinkage appear on the casting surface as dips or holes.
- Closed Shrinkage Defects: Closed shrinkage defects show up as holes inside the casting. Some can be seen while others cannot.
- Warping: Warping happens during solidification or after. This defect changes the shapes and dimensions of the casting.
Causes of Shrinkage Defects
Shrinkage defects happen when the molten metal in the mold does not have a uniform temperature. This can be due to uneven solidification or when the molten metal is too hot.
Remedies for Shrinkage Defects in Casting
Uneven solidification can be prevented by ensuring a continuous flow of molten metal into the mold. This is possible if you use runners and gating systems with risers to direct the molten metal. These channels ensure the even distribution of the molten metal into the mold.
Accordingly, you can add padding to the mold. This widens narrow pieces attached to thicker parts to ensure even distribution of molten metal before other parts start solidifying. Alternatively, you can use cooling coils, ribs, or chills in the mold for faster heat dispersion.
2. Gas Porosity Defects in Casting

Gas porosity defects happen when the cast metal traps gases like oxygen, nitrogen, or hydrogen. The fault usually appears on the casting surface as holes and cavities. Here are examples of gas porosity defects:
- Pinholes: These are holes that appear on the mold’s outer cope part. They particularly happen on poorly vented pockets.
- Open holes: These are blowholes that appear on the casting surface. They are always easy to detect.
- Subsurface blowhole: These are larger cavities seen inside the casting. Blowholes cannot be detected easily.
Remedies for Gas Porosity Defects in Casting
All gas porosity defects can be prevented by using dry and permeable sand to make molds. Accordingly, it is advisable to use coarser sand.
Alternatively, the foundry should apply good melting practices. This can be achieved by melting the metal in a vacuum to prevent air.
3. Defects in the Mold Material
Mold material defects happen in the mold material. Additionally, these irregularities can also occur when the mold design has issues. Examples of mold material defects include:
- Cuts and washes: These are caused by the molten metal eroding the mold part. They often appear as bulges on the surface of the casting.
- Swells: These are swellings on the final product.
- Drops: These defects can be seen as bumps on the casting surface.
- Runout: Runouts are a result of a leaking mol.
- Fusion: These may be seen as glassy crusts on the metal surface.
- Metal penetration: Molten metal can sometimes penetrate the mold, mainly when the sand grains are large and loose. This leads to a rough surface of the final piece.
- Rat tails: This defect can be seen as running lines along the surface of the final part.
Remedies for Mold Material Defects in Casting
The most straightforward way to prevent mold material defects in casting is to ensure every mold receives enough ramming to hold the molten metal.
4. Defects in Pouring Metal
Unlike any other defect, pouring metal defects happen when the temperatures are too low. Examples include:
- Cold shot: This defect appears as drops that are loosely attached to the final piece.
- Cold shuts: These irregularities happen when the molten metal flows into the mold from many sections. Since the temperatures are low, they do not merge seamlessly into the final piece.
- Misruns: They are almost similar to cold shuts. This happens when the molten metal starts solidifying before filling the entire mold.
Remedies for Pouring Metal Defects in Casting
The most straightforward way to prevent defects of metal pouring in casting is to ensure the molten metal is warm enough until it fills the entire mold. This can be achieved by redesigning the gating system to speed up the flow of molten metal to the mold.
5. Metallurgical Defects in Casting
These defects appear when there are problems with the casting metal. The most common examples include:
- Slag inclusion: This defect happens when the casting metal is not adequately cleared of slag, leading to impurities in the final piece.
- Hot tears: Also referred to as hot cracks, this defect happens when the cooling piece contracts and pulls apart.
- Hot spots: When other parts of the metal cool faster than the surrounding areas.
Remedies for Metallurgical Defects in Casting
The best remedy is to use well-designed molds to enhance even cooling of the molten metal. Additionally, you should consider removing slag properly from the molten metal. This can be achieved by adding a ceramic filter to the gating system.
6. Defects in the Casting Shape
Casting shape defects in casting can appear as mismatches or flashes.
- Mismatches: This happens when various parts of the finished piece come out misaligned.
- Flash: Flash may appear as extra material to the surface of the finished piece.
Remedies for Casting Shape Defects
Preventing casting shape defects involves ensuring plate pattern mounting and alignment are the same. Accordingly, you may want to reassemble the entire mold.
Final Thoughts
Knowing all potential casting defects and their remedies is an essential step to ensuring casting quality. This article will help you set apparent defect tolerance and quality expectations by knowing the casting problems, their causes, and solutions.