Contents
The Different Types of Casting Processes Used in Manufacturing
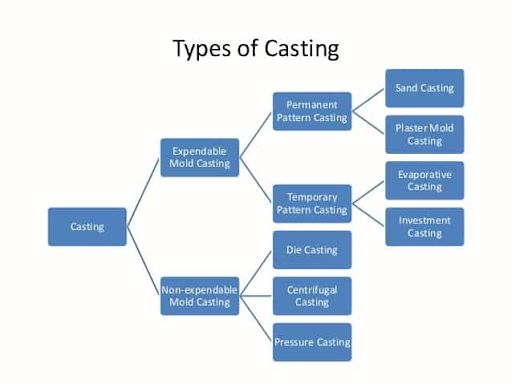
Image Source: learnMech
Manufacturing processes are highly complex and require a lot of planning, preparation, and attention to detail.
There are many different ways to execute the casting process, all of which have their own pros and cons.
Understanding the various casting processes used in manufacturing is essential to creating an optimally functioning production environment.
The type of casting process you choose will depend on your unique production needs, as well as the properties of the components being manufactured.
Casting may also be referred to as foundry or molding
Depending on your industry, there are several types of casting processes commonly used in manufacturing.

What is a Casting Process in Manufacturing?
A casting process is a manufacturing method associated with the creation of metal components by pouring molten metal into a mold
There are many different casting processes used in manufacturing, and each one has its own unique set of benefits and challenges.
The type of casting process used will depend on the desired outcome, as well as the properties of the metals you are working with.
Casting is used to manufacture many different types of parts, including automobile engine components, machine parts, complex metal joints, pipes, hardware, moulds, and many more.
Investment Casting
Investment casting is a casting process commonly used in the creation of complex components.
It is suitable for manufacturing large castings that require intricate shapes and fine tolerances.
Investment casting wax is suitable for parts made from a wide range of alloys, including steels, cobalt, nickel, and iron, as well as non-ferrous metals such as copper, brass, and bronze.
Investment casting foundry is a type of casting process known as “Lost Wax” casting.
This means that a wax model of the desired casting is first created.
The wax model is then covered with a substance called a “Slurry” that hardens around the wax model and forms a mold
A metal alloy is then poured into the mold, filling it completely.
Once the metal has cooled and hardened, the mold is broken to reveal the casting within.
Investment casting is a highly complex and delicate process, but it is also very precise and can produce high-quality, fine-finish castings.
You can easily find investment casting suppliers in China and find out everything about it.
This will of course include the investment casting price.
Read deeper on this website as we will discuss the investment casting advantages and disadvantages. You can also download our investment casting pdf.
You can also check out the investment casting Wikipedia for more details.
Centrifugal casting
Centrifugal casting is a casting process used to create cylindrical parts. The process is typically used to manufacture pipes, sewer lines, and other long, cylindrical components.
The process begins by pouring molten metal into a rotating mold. The centrifugal force of the rotating mold causes the metal to flow outward, creating a long, thin, cylindrical shape.
The mold is then rotated in the opposite direction to create the walls of the pipe. The mold is then opened and the casting is removed.
The casting may then be subjected to cold-working to achieve the desired dimensions and surface finish.
Vacuum Casting
Vacuum casting involves pouring liquid metal into a rubber mold, which then creates a positive image of the mold.
The mold can be made from a variety of materials, including rubber and plaster.
Once the liquid metal has hardened, the mold is removed to reveal the finished product. Vacuum casting is typically used to produce small, thin, or irregularly shaped components.
Plaster casting
Plaster casting is a type of investment casting that is often used for low-volume production with complicated parts.
After creating the wax model, it is coated in a type of plaster that hardens as it dries.
The plaster model is then used to create a mold, which is further treated with a refractory material to create the final mold.
When the mold is completely dried, the plaster materials are removed, and the mold is ready for casting.
The plaster materials are removed with extreme caution as they are very fragile. Plaster casting is typically used for low-value, low-complexity parts.
Shell casting
Shell casting is a casting process used to create hollow parts. A molten metal is poured into a mold and allowed to cool.
The mold is then opened and the shell is removed and placed in a furnace to remove any internal oxides.
The shell is then filled with molten metal to create a completed casting. Shell casting is commonly used to make small castings of intricate shapes.
It is often used to manufacture engine valves, dies, and other small machine parts.
The process of shell casting allows the creation of parts with a thin wall thickness and large interior cavity, which may be impossible to create through other casting processes.
Sand casting
Sand casting is a casting process involving the pouring of molten metal into a sand mold.
Castings made using this process are typically large and simple. Sand castings are also usually made from unalloyed or low-alloy steels.
A commonly used sand casting is the “Lost Wax” process, where a wax model is created and then covered with sand before being melted away.
Sand casting is a very simple and inexpensive casting process that is most often used to produce large castings with simple geometry.
It is often used to make machine parts, gears, and automobile engine components.
Die-casting
Die-casting is a casting process that creates a positive impression of a part in a refractory mold.
The mold is made of a high-temperature-resistant material, such as graphite or ceramics. The molten metal is poured into the mold and allowed to cool. The mold is then opened, and the casting is removed.
Die-casting is typically used for the production of small, simple parts with uniform geometry.
It is often used to manufacture small metal parts, such as automobile engine components, nails and screws, complex machine parts, and precision hardware.
Gravity Die Casting
Gravity die casting is a casting process that uses a rotating mold to create a casting that is thicker on the bottom than the top. The molten metal is poured into a rotating mold and allowed to cool.
The mold is then opened, and the casting is removed. Gravity die casting is commonly used to manufacture small, simple castings with a uniform wall thickness.
It is often used to create engine valves, automobile components, and other small, simple parts.
Gravity die casting is typically used for the casting of non-ferrous metals such as copper, zinc, and tin. It is also sometimes used for the casting of low-alloy steels.
Precision metal casting
Precision metal casting is a highly-controlled casting process that starts with the creation of a wax model. This model is then coated in refractory material and subjected to heat to create a ceramic mold.
The mold is then flooded with molten metal, and after some cooling time, the mold materials are removed, leaving behind a porous model.
The porous model is then subjected to a process called “degassing” to remove all remaining air bubbles.
After degassing, the model is ready for finishing and machining.
This casting process is most commonly used for high-value, high-complexity parts.
Choose China investment casting manufacturers
Investment casting is the most widely used casting process because of the durability and intricate detail it produces.
So, where should I get my investment casting done?
This is a question that you are likely to ask with regard to the investment casting disadvantages and benefits.
Of course, you should choose a reputable investment casting factory for the job.
There are various investment casting products that you can get from the supplier or manufacturer.
Once you get your investment casting drawing, the company will send the details, such as the investment casting quotation.